Introduction
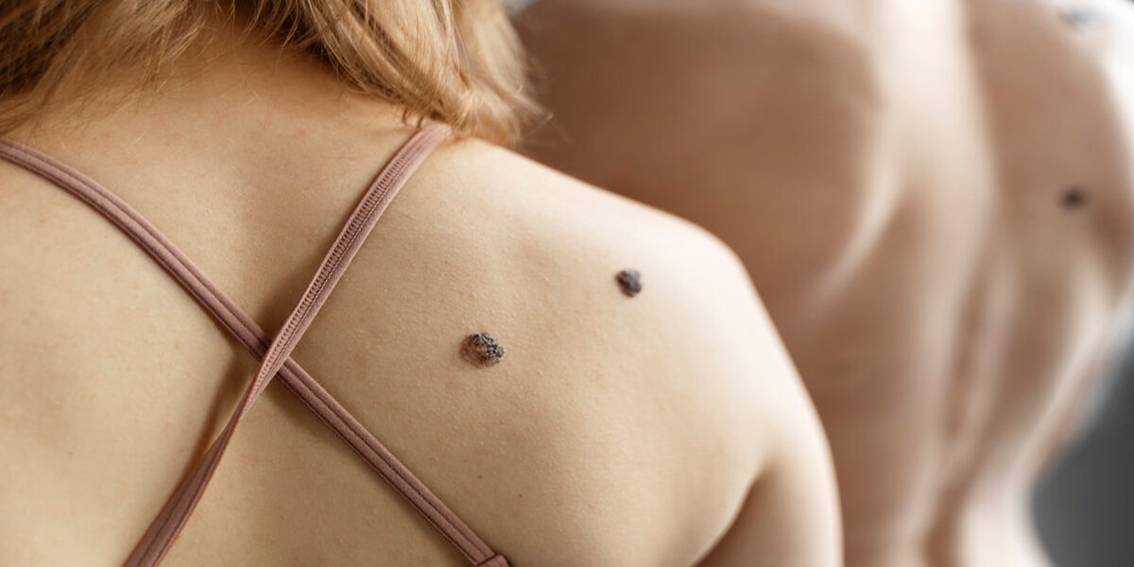
Skin Moles are common skin growths that usually appear in childhood or adolescence. While most moles are harmless, changes in their appearance can sometimes signal underlying issues.
What is Spiloi or Skin Moles on the skin
“Spiloi” (σπίλοι) is the Greek word for moles on the skin. Moles, medically known as nevi, are small, pigmented spots on the skin that form when melanocytes (the cells that produce pigment) grow in clusters. They are usually brown or black and can appear anywhere on the body.
Key Characteristics of Moles
Appearance: Moles can be flat or raised, smooth or rough, and may have hair growing from them.
Colour: They are typically brown or black but can also be skin-coloured, pink, red, or blue.
Size: Most moles are small, usually less than 6mm in diameter (about the size of a pencil eraser).
Shape: They are generally round or oval with even borders.
Normal vs. Atypical Moles
Normal moles are typically small, round, and evenly coloured. Atypical moles, or dysplastic nevi, may have irregular shapes, uneven borders, or multiple colours. These moles require closer monitoring.
Signs of Concern
Changes in size, shape, colour, or texture of a mole can be a cause for concern. Other warning signs include itching, bleeding, or crusting. These changes may indicate skin conditions that need medical attention.
Risk of Melanoma
Melanoma, a type of skin cancer, can develop from existing moles or appear as new growths. Early detection is crucial, as melanoma can spread quickly if left untreated.
ABCDE Rule for Monitoring
The ABCDE rule helps identify suspicious moles
Asymmetry: One half does not match the other.
Border: Edges are irregular or blurred.
Colour: Multiple colours or uneven shading.
Diameter: Larger than 6mm (about the size of a pencil eraser)
Evolving: Changes in size, shape, or colour over time.
Importance of Regular Checks
Regular self-examinations can help detect changes early. Use a mirror to check hard-to-see areas or ask someone for assistance. Annual skin checks by a dermatologist are also recommended.
Sun Exposure and Prevention
Excessive sun exposure increases the risk of mole changes and skin cancer. Use sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, wear protective clothing, and avoid peak sun hours to protect your skin.
When to See a Dermatologist
If you notice any concerning changes in a mole, consult a dermatologist immediately. They may perform a biopsy to determine if further treatment is needed or remove in some cases
Treatment Options
If a mole is found to be abnormal, a dermatologist may recommend removal. This can be done through excision, shaving, or laser treatment, depending on the mole’s characteristics.
Conclusion
While most moles are harmless, monitoring them for changes is essential. Early detection of suspicious moles can prevent serious skin conditions. Regular self-checks and professional evaluations are key to maintaining healthy skin.